Smart lighting
Contents |
[edit] What is smart lighting?
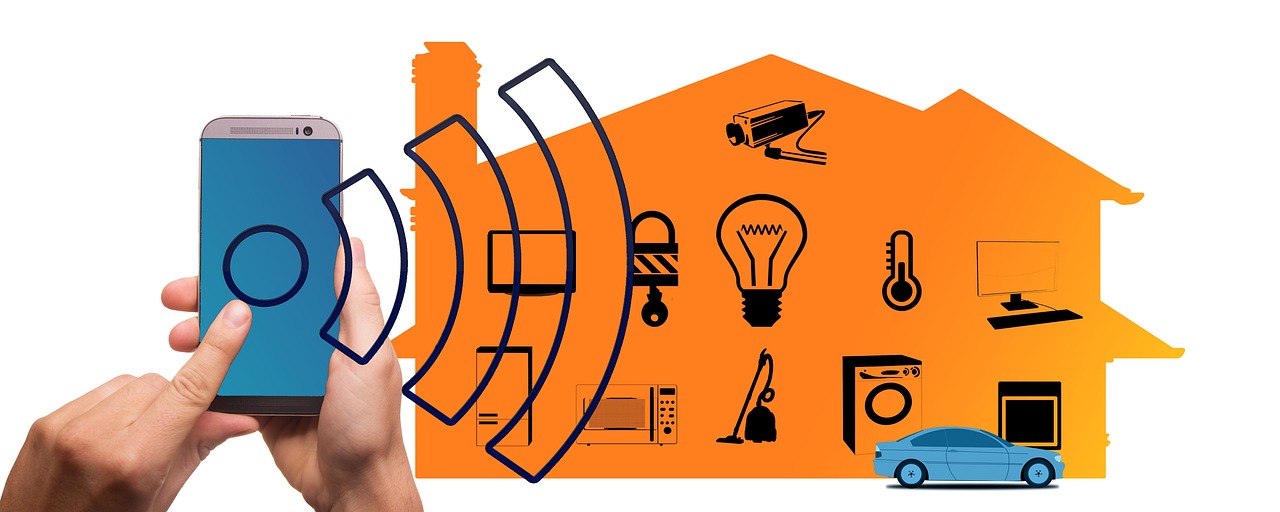
Smart lighting allows users to control and customise the lighting in a building using remote devices such as smartphones or tablets. It is designed to be convenient, energy-efficient, and programmable, and can be used to create a variety of lighting environments for different tasks or occasions.
[edit] What are the advantages of smart lighting?
One of the main advantages of smart lighting its ability to control lighting remotely. This can be done using a smartphone or tablet, or through a smart home hub. With smart lighting, users can turn lights on or off, dim them, or change their colour from anywhere with an internet connection. This can be particularly useful when the user is away from the building, as it allows them to turn the lights off if they forgot to do so before leaving, or to turn them on when they are on their way home.
Smart lighting is also energy-efficient. Many smart bulbs use LED technology to reduce energy consumption. Additionally, the ability to control lighting remotely means that users can turn off lights that are not needed.
Many smart bulbs can be programmed to change colour, allowing users to create a variety of different lighting environments for different tasks or occasions. For example, a user might choose a softer, warmer light for relaxation or a cooler, brighter light for tasks such as reading or cooking.
Smart lighting can be integrated with other smart devices, such as thermostats and security systems, allowing control all of a property's systems from one central location.
Smart lighting can also be programmed to turn on and off at certain times, creating the illusion that someone is home even when they are not. This can deter burglars and increase overall safety and security.
[edit] What are the disadvantages of smart lighting?
Smart lighting systems can be expensive to instal, especially if you want to retrofit your entire home with smart bulbs. The cost of smart bulbs can also be higher than traditional bulbs. They can also be complex to set up and use, especially for people who are not tech-savvy. It may take some time to learn how to use all of the features and functions of a smart lighting system.
Most smart lighting systems require a central hub to function. If this hub fails or loses power, the smart lighting system may not work properly. Smart lighting systems also require an internet connection to function properly. If the internet goes down, the smart lighting system may not work properly.
Smart lighting systems may not be compatible with older homes or buildings that do not have the necessary wiring or infrastructure in place.
Some people may also be concerned about the privacy implications of having a smart lighting system that can be controlled remotely.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Commercial lighting.
- General lighting v task lighting.
- Light fitting.
- Lighting and energy efficiency.
- Lighting control.
- Lighting for circadian rhythms.
- Lighting in commercial buildings.
- Lighting of construction sites.
- Lighting.
- Natural light.
- Smart lighting market to 2020.
- Smart office lighting.
- Types of lamp.
- Types of lighting.
[edit] External references
- "Smart lighting explained: What it is and why you should care." CNET. https://www.cnet.com/news/smart-lighting-explained-what-it-is-and-why-you-should-care/
- "Smart lighting: A beginner's guide." Techradar. https://www.techradar.com/uk/news/smart-lighting-a-beginners-guide
- "Smart Lighting: The Benefits and Drawbacks." Electronic House. https://www.electronichouse.com/smart-home/smart-lighting-the-benefits-and-drawbacks/
Featured articles and news
Resident engagement as the key to successful retrofits
Retrofit is about people, not just buildings, from early starts to beyond handover.
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.




















Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, or to suggest changes, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.